大家好,我是烤鸭:
根据官方文档翻译并精简部分内容。建议有时间的朋友下载原版查看,全文106页pdf,快的话1-2天就能看完。自己翻译的有些地方可能不完整,欢迎指正。
-
官方pdf下载,需登录:
-
https://www.mysql.com/cn/why-mysql/presentations/tune-mysql-queries-performance/
-
csdn下载地址:
-
https://download.csdn.net/download/angry_mills/10953302
-
简化版地址:
-
https://blog.csdn.net/Angry_Mills/article/details/88081834
MySQL Optimizer
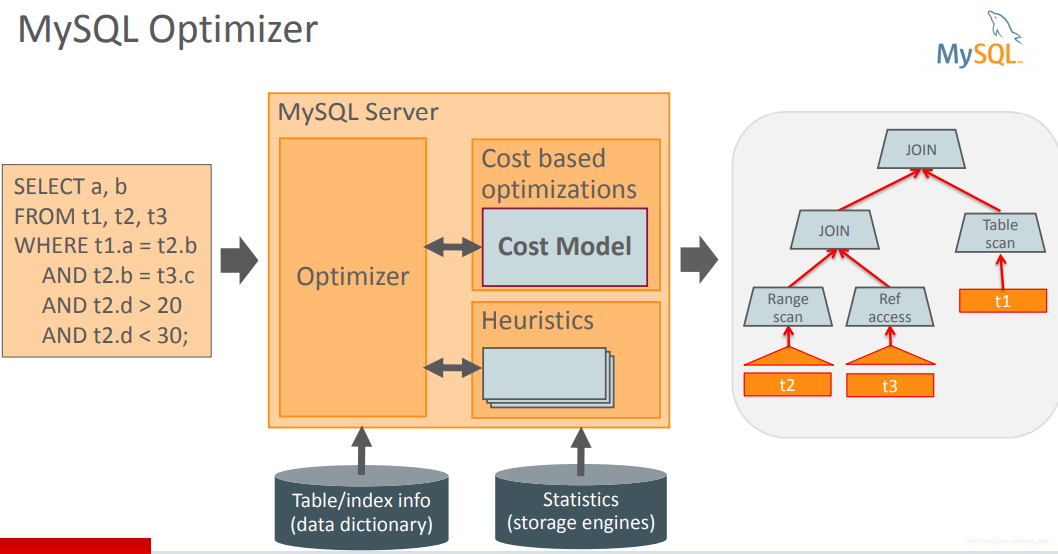
通常的想法:
- Assign cost to operations
- Assign cost to partial or alternative plans
- Search for plan with lowest cost
- Cost-based optimizations
- Access method Subquery strategy Join order
mysql优化的特点:
- Produce the query plan that uses least resources IO and CPU
- Optimizes a single query No inter-query optimizations
- Produces left-deep linear query execution plan
Optimizer Cost Model 优化器成本模型
图 Optimizer Cost Mode
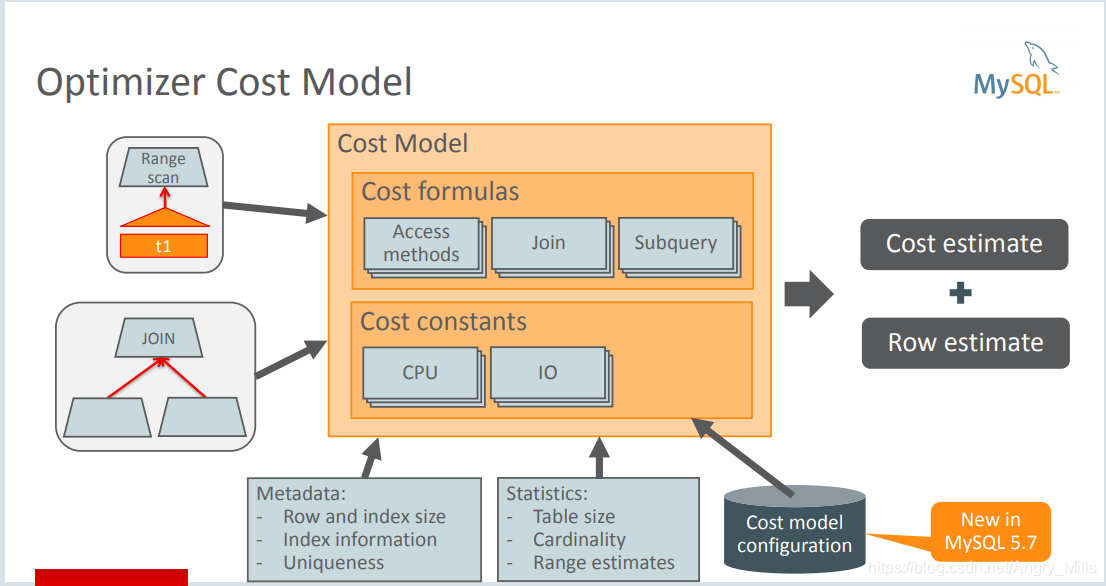
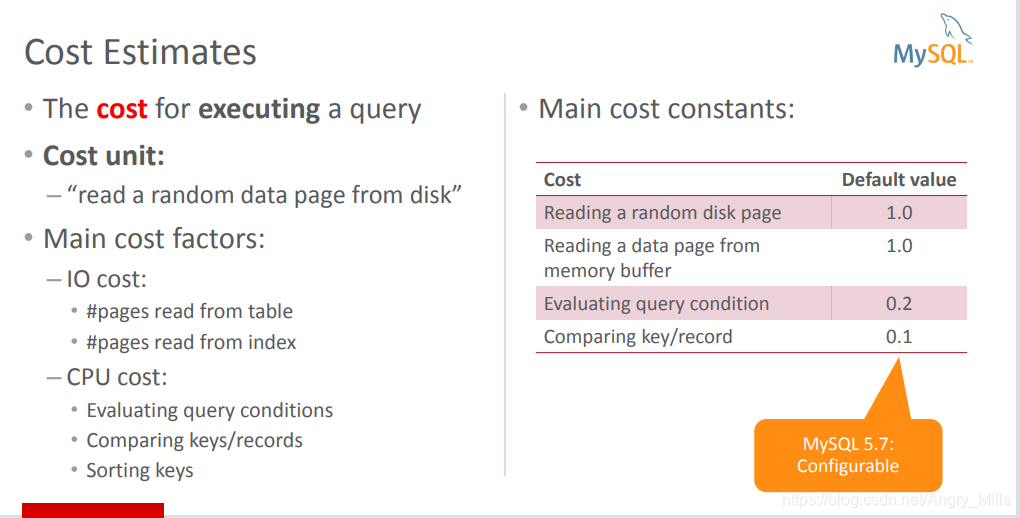
Cost Estimates
- Cost unit:
“read a random data page from disk”
Main cost factors: - IO cost:
pages read from table:
pages read from index: - CPU cost:
Evaluating query conditions:
Comparing keys/records :
图 Cost Estimates
Cost Model Example
- Table scan:
- IO-cost: #pages in table * IO_BLOCK_READ_COST
- CPU cost: #rows * ROW_EVALUATE_COST
- Range scan (on secondary index):
- IO-cost: #rows_in_range * IO_BLOCK_READ_COST
- CPU cost: #rows_in_range * ROW_EVALUATE_COST
图 Cost Model Example

图 Cost Model Example: Optimizer Trace
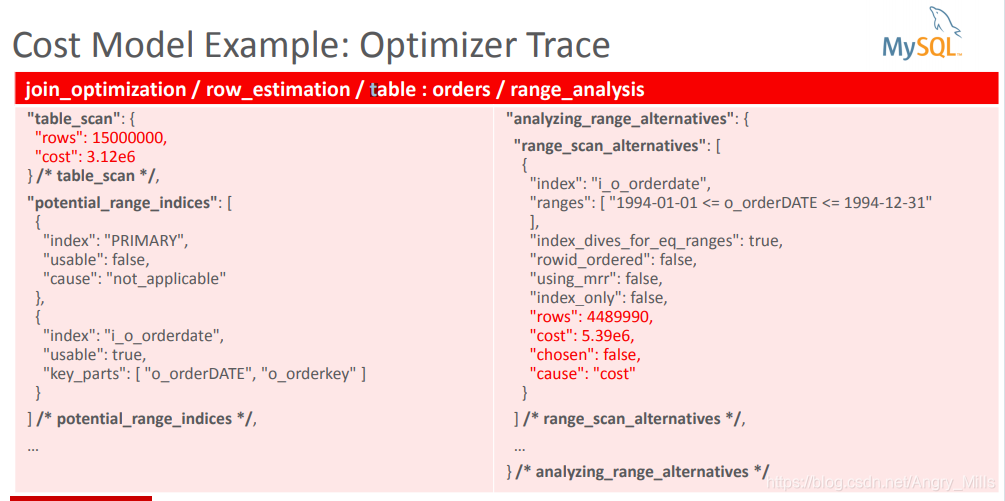
图 Cost Model vs Real World
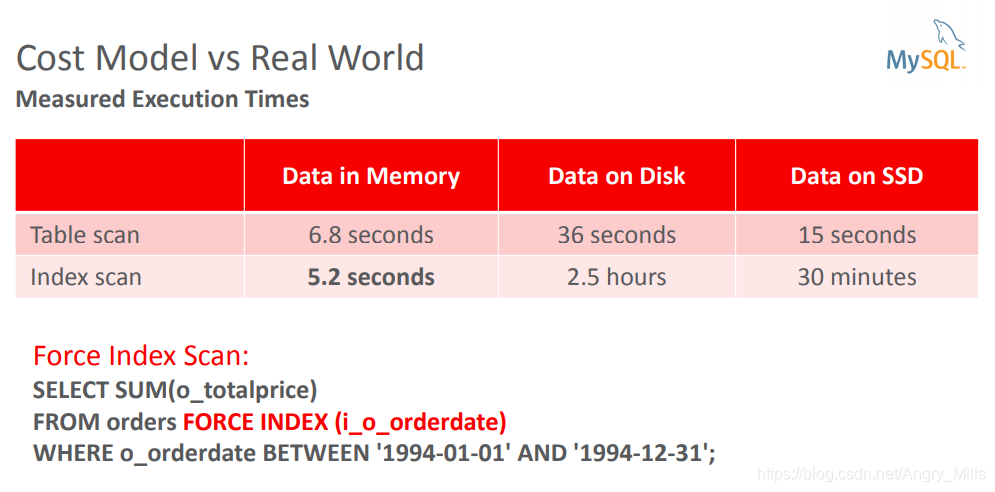
图 Cost Model Performance Schema
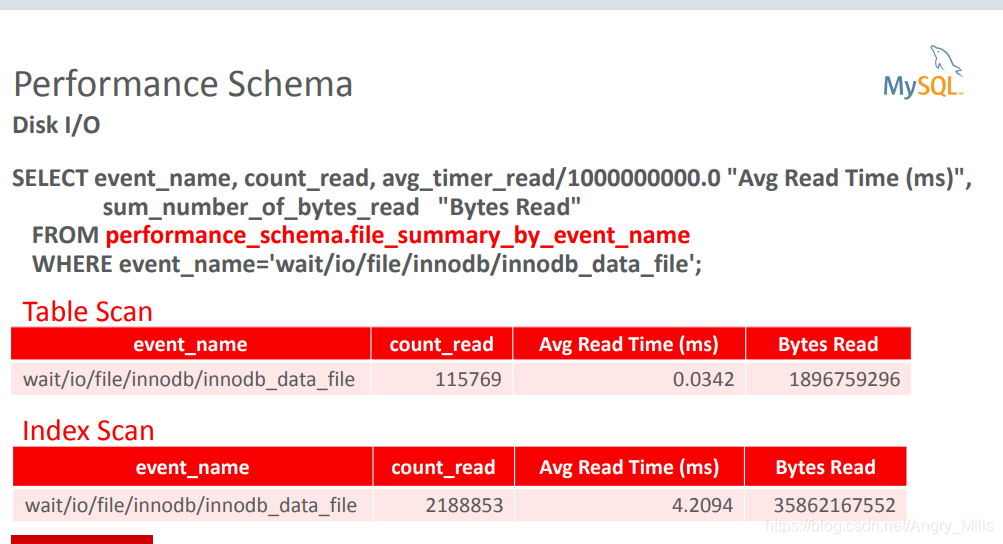
- Useful tools
- MySQL Enterprise Monitor (MEM), Query Analyzer Commercial
product - Performance schema, MySQL sys schema
- EXPLAIN
- Tabular EXPLAIN 表格式EXPLAIN
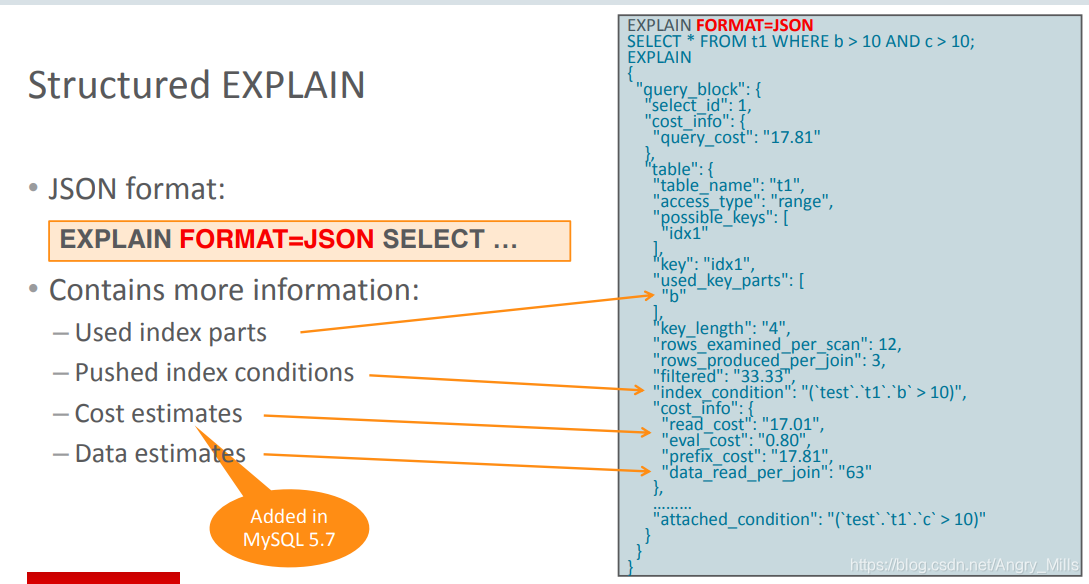
- Structured EXPLAIN (FORMAT=JSON)结构式EXPLAIN 图*2

- Visual EXPLAIN (MySQL Workbench)
- Optimizer trace
- Slow log
- Status variables (SHOW STATUS LIKE ‘Sort%’)
MEM 图形化界面,收费的,暂时不考虑了,看下面的例图
图 Query Analyzer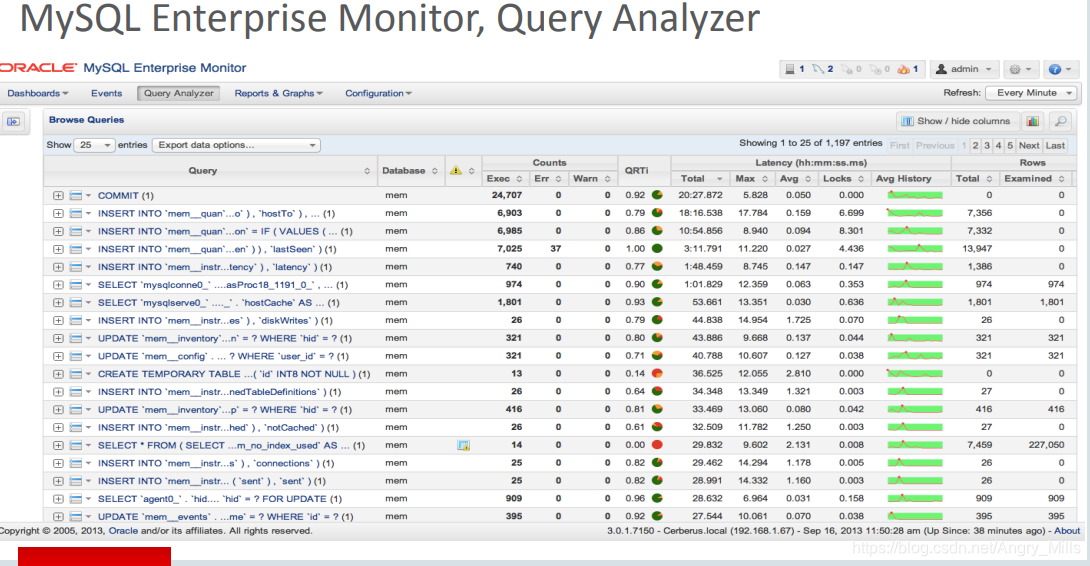
图 Query Analyzer Query Details
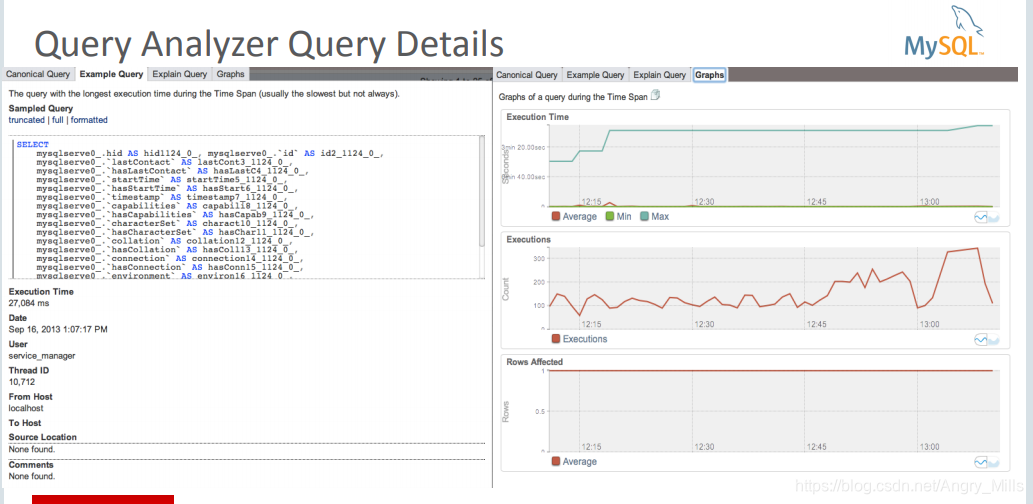
Performance schema
一些有用的表:
-
events_statements_history,events_statements_history_long Most
recent statements executed
-
events_statements_summary_by_digest Summary for similar statements
(same statement digest)
-
file_summary_by_event_name
-
Interesting event: wait/io/file/innodb/innodb_data_file
-
table_io_waits_summary_by_table
-
table_io_waits_summary_by_index_usage
-
Statistics on storage engine access per table and index
Statement events
-
Tables:(Current statement for each thread)
-
events_statements_history (10 most recent statements per thread)
-
events_statements_history_long (10000 most recent statements)
-
Statement digest
-
Normalization of queries to group statements that are similar to be
grouped and summarized:
events_statements_summary_by_digest
MySQL sys Schema
- A collection of views, procedures and functions, designed to make
reading raw Performance Schema data easier
- Implements many common DBA and Developer use cases
- File IO usage per user
- Which indexes is never used?
- Which queries use full table scans?
- Examples of very useful functions:
- format_time() , format_bytes(), format_statement()
- Included with MySQL 5.7
- Bundled with MySQL Workbench
MySQL sys Schema MySQL 系统计划
- statement_analysis :Lists a normalized statement view with aggregated
statistics, ordered by the total execution time per normalized
statement ()
EXPLAIN Understand the query plan
图 EXPLAIN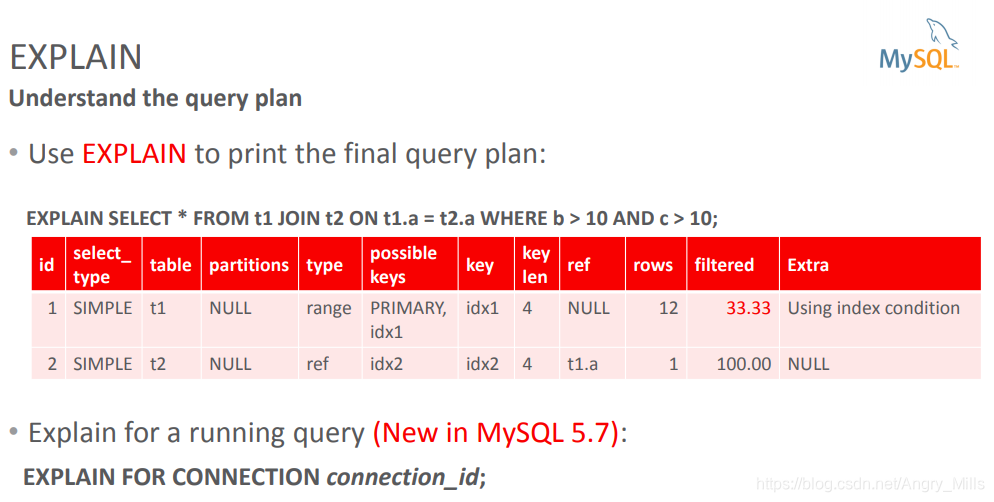
Structured EXPLAIN ()
图 Structured EXPLAIN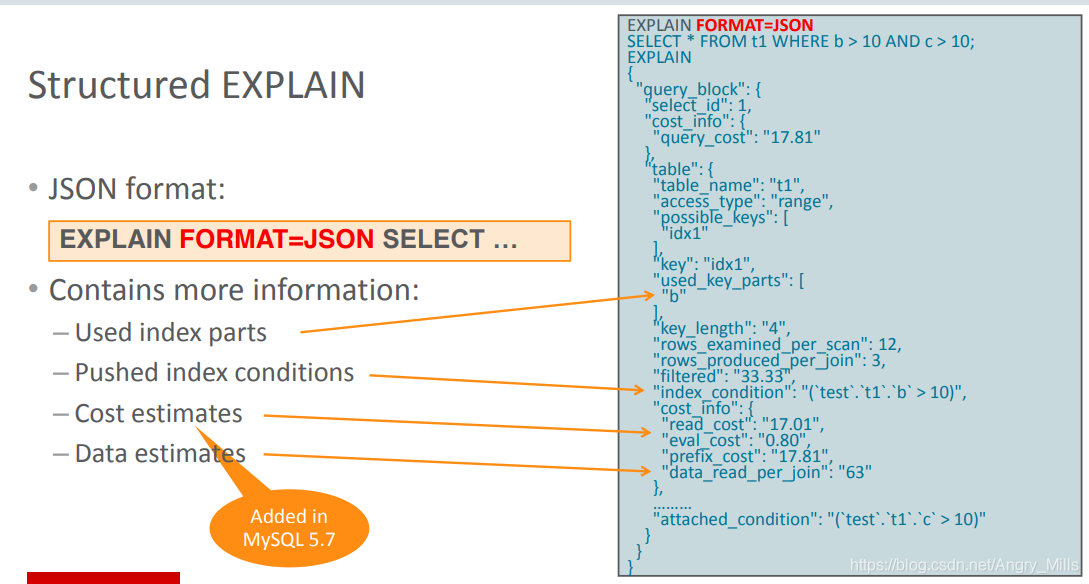
Contains more information:
- Used index parts
- Pushed index conditions
- Cost Estimates
- Data estimates
图 Structured EXPLAIN
图 MySQL sys Schema Example

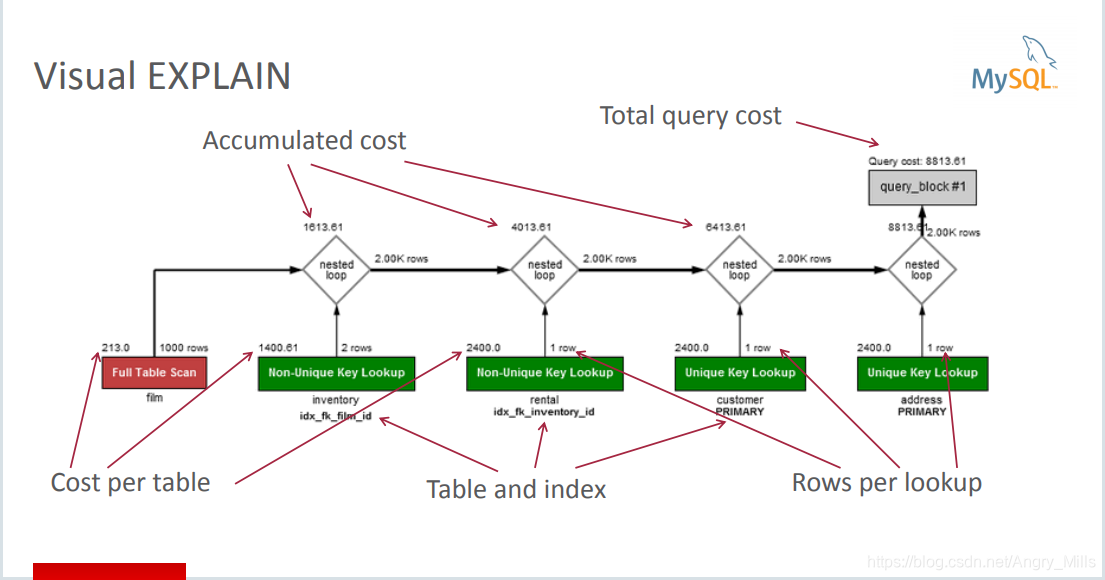
Visual EXPLAIN 可视化EXPLAIN
图 Visual EXPLAIN
Optimizer Trace: Query Plan Debugging
- EXPLAIN shows the selected plan EXPLAIN
- Optimizer trace shows WHY the plan was selected
图 Optimizer Trace Debugging
- Finding the optimal method to read data from storage engine
- For each table, find the best access method:
- Check if the access method is useful
- Estimate cost of using access method
- Select the cheapest to be used
- Choice of access method is cost based
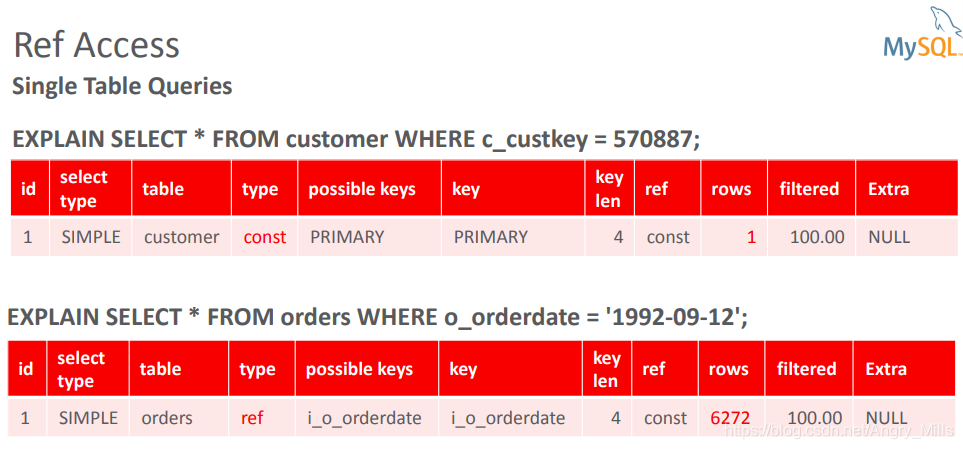
- Ref Access
- Single Table Queries
图 Ref Access Single Table Queries
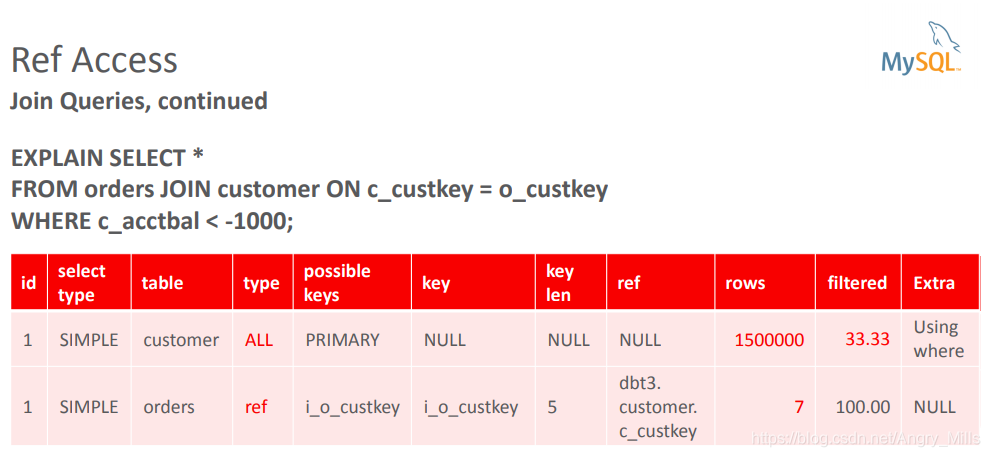
Join Queries 连接查询

图 Ref Access Single Join Queries

Join Queries, continued
图 Ref Access Join Queries continued
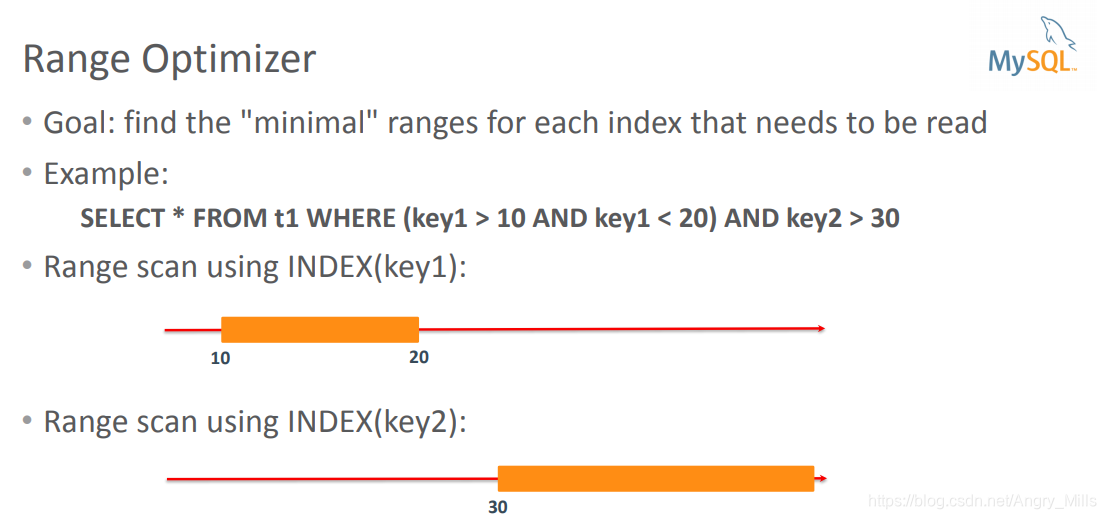
- Range Optimizer
- Goal: find the “minimal” ranges for each index that needs to be read
Example:
图 Ref Access Range Optimizer
- Range Optimizer, cont
- Range optimizer selects the “useful” parts of the WHERE condition:
- Conditions comparing a column value with a constant:
- Nested AND/OR conditions are supported
- Result: list of disjoint ranges that need to be read from index:
- Cost estimate based on number of records in each range:
- Record estimate is found by asking the Storage Engine (“index dives”)
Optimizer Trace show ranges
图 Optimizer Trace show ranges

Range Optimizer: Case Study
- Why table scan?
图 Range Optimizer Case Study1
possible keys NULL 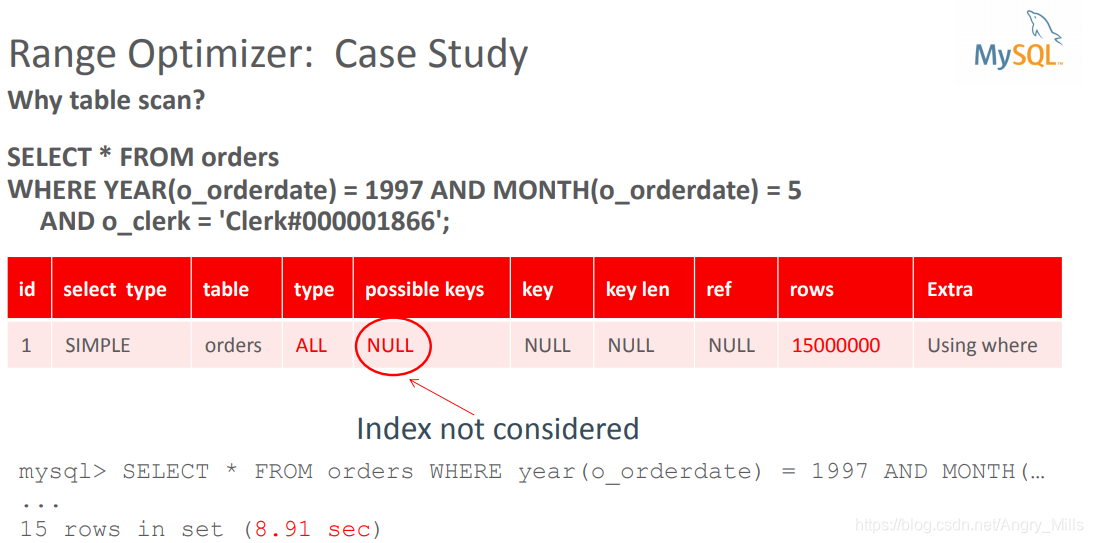
- Some Reasons Why Index can not be Used
-
ndexed column is used as argument to function
-
Looking for a suffix
-
First column(s) of compound index NOT used
b = 10 when index defined over (a, b)
-
Type mismatch
-
Character set / collation mismatch
案例学习:
- Rewrite query to avoid functions on indexed columns
例如: i_o_orderdate
图 Case Optimizer Case Study2
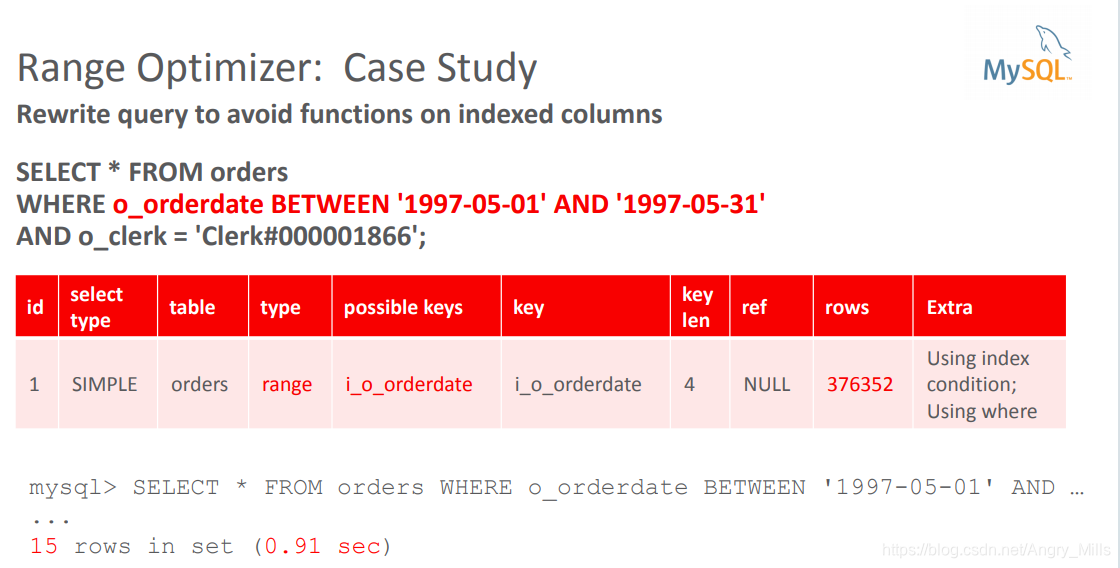
- Adding another index
图 Range Optimizer Case Study3

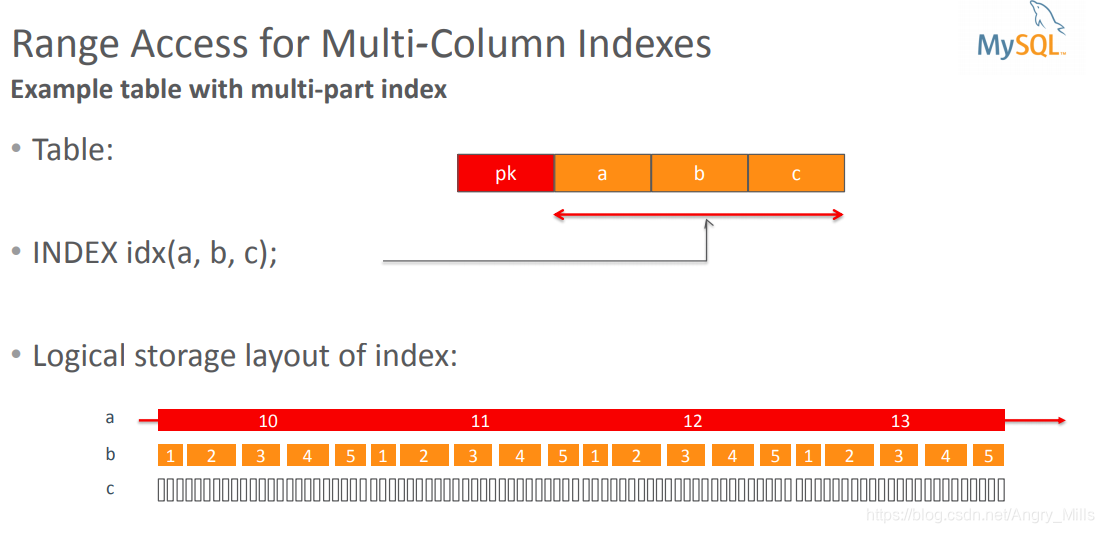
-
Range Access for Multi-Column Indexes
-
Example table with multi-part index
-
Logical storage layout of index:
图 Range Access for Multi-Column Indexes
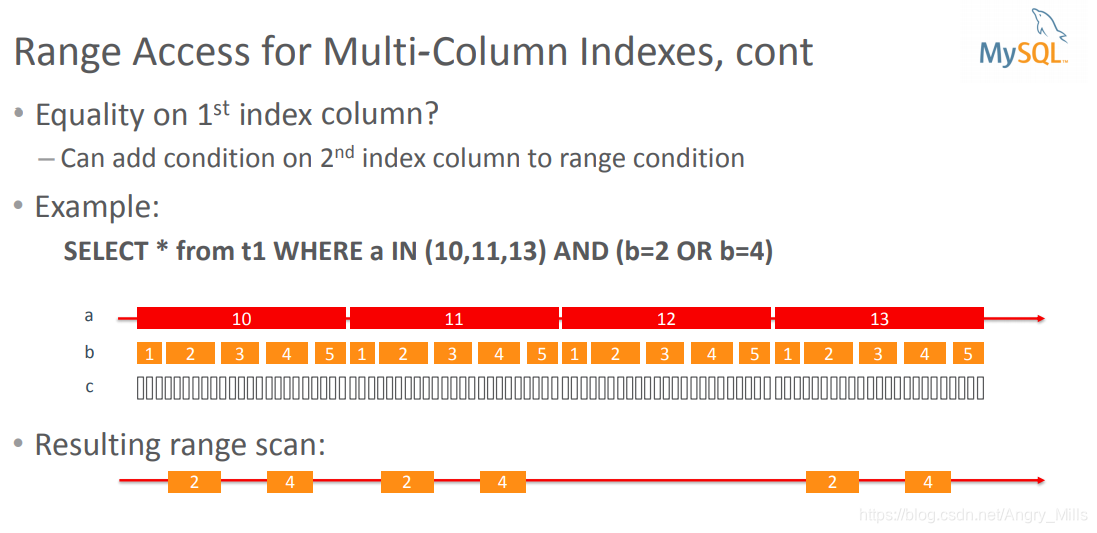
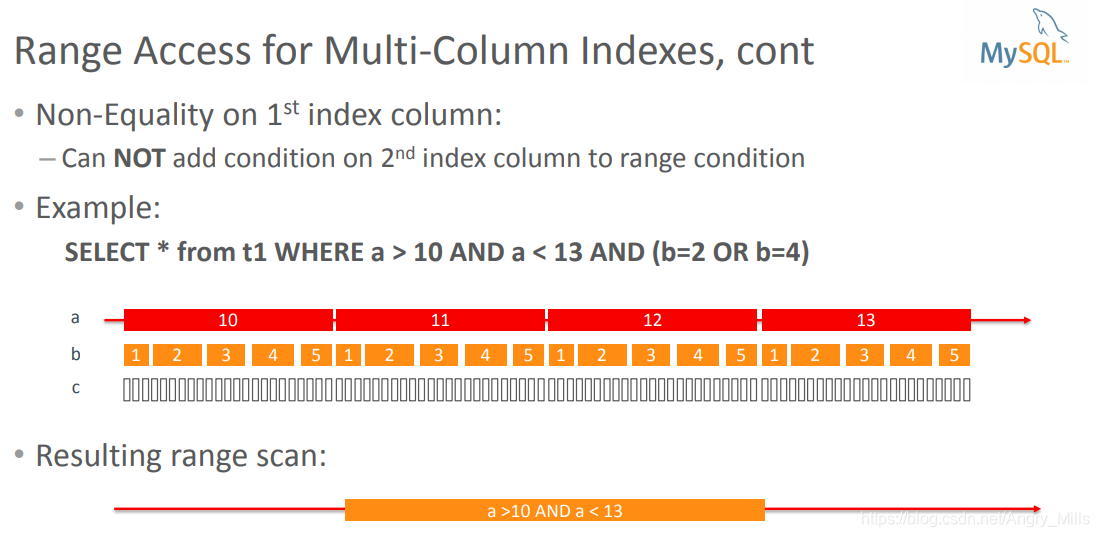
Range Access for Multi-Column Indexes, cont
Resulting range scan
图 Range Access for Multi-Column Indexes, cont
Resulting range scan
图 Range Access for Multi-Column Indexes, cont+
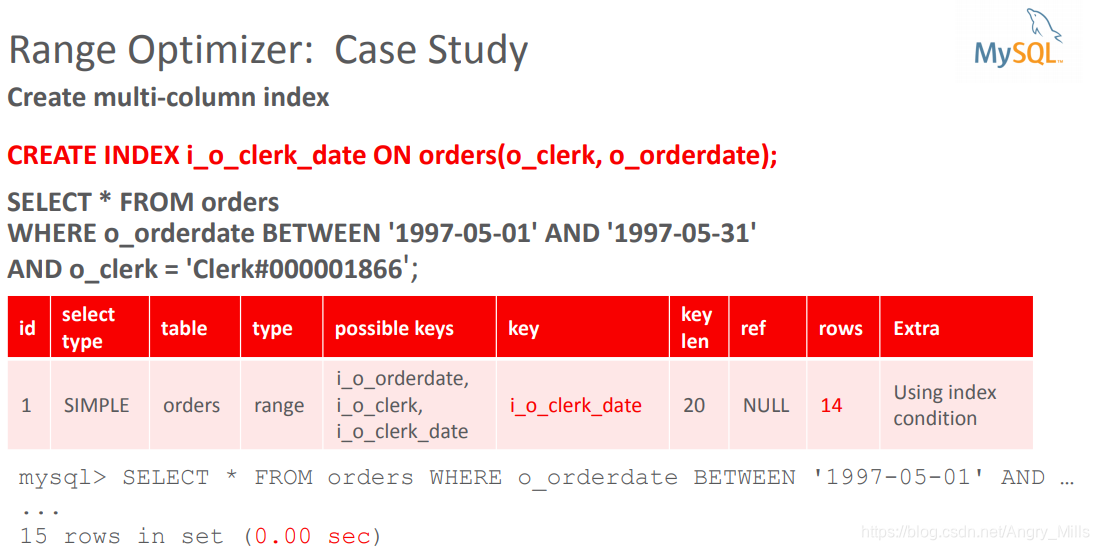
案例学习:
- Create multi-column index
图 Range Optimizer Case Study4
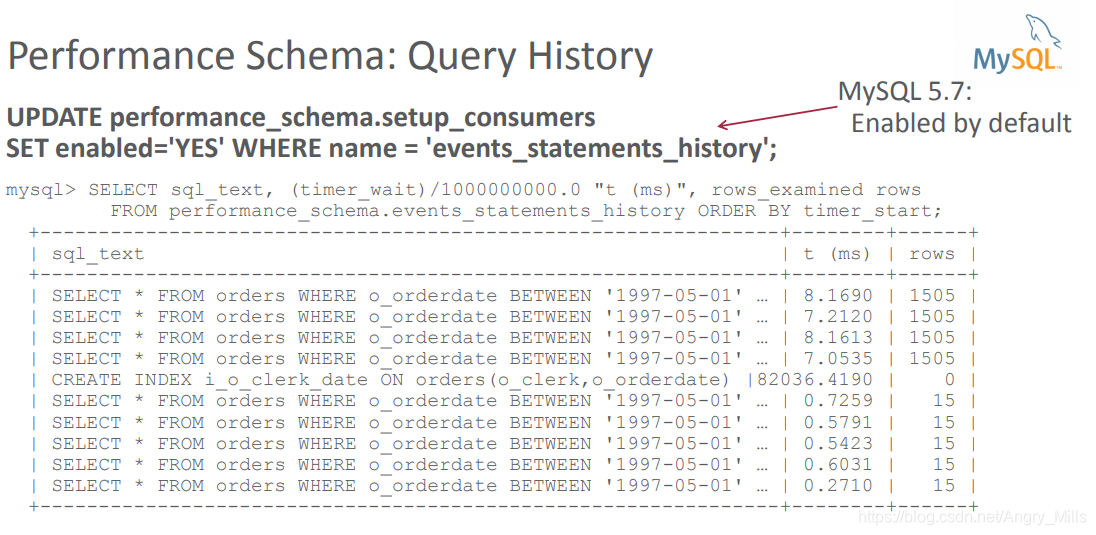
Performance Schema: Query History
图 Performance Schema: Query History
Index Merge
- Uses multiple indexes on the same table
- Implemented index merge strategies
- Index Merge Union
- OR-ed conditions between different indexes
- Index Merge Intersection
- AND conditions between different indexes
- Index Merge Sort-Union
- OR-ed conditions where condition is a range
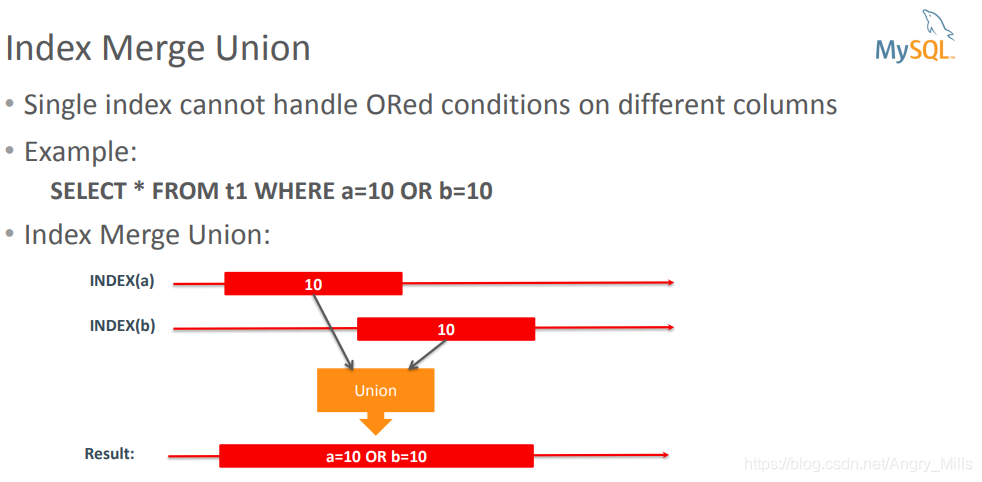
Index Merge Union
- Single index cannot handle ORed conditions on different columns
例如:
图 Index Merge Union
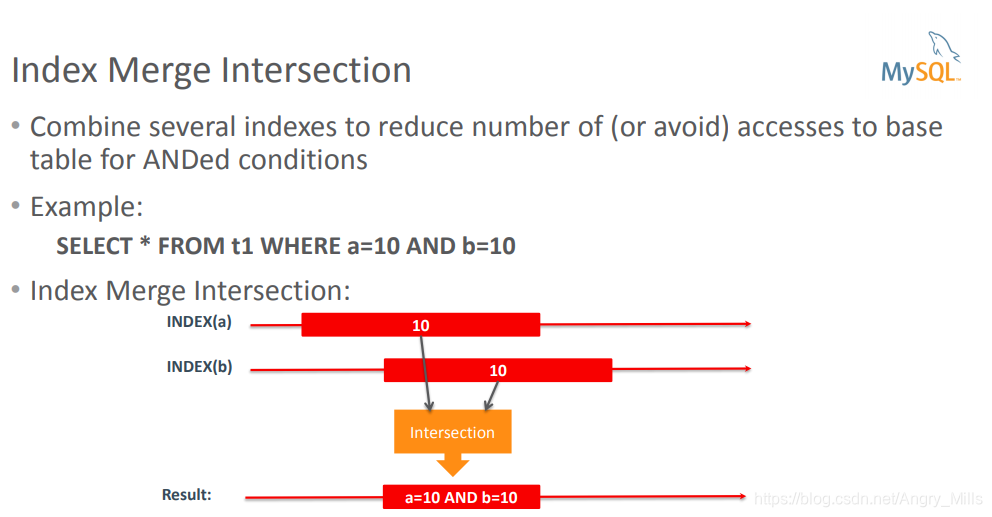
Index Merge Intersection
- Combine several indexes to reduce number of (or avoid) accesses to base table for ANDed conditions
例如:
图 Index Merge Intersection
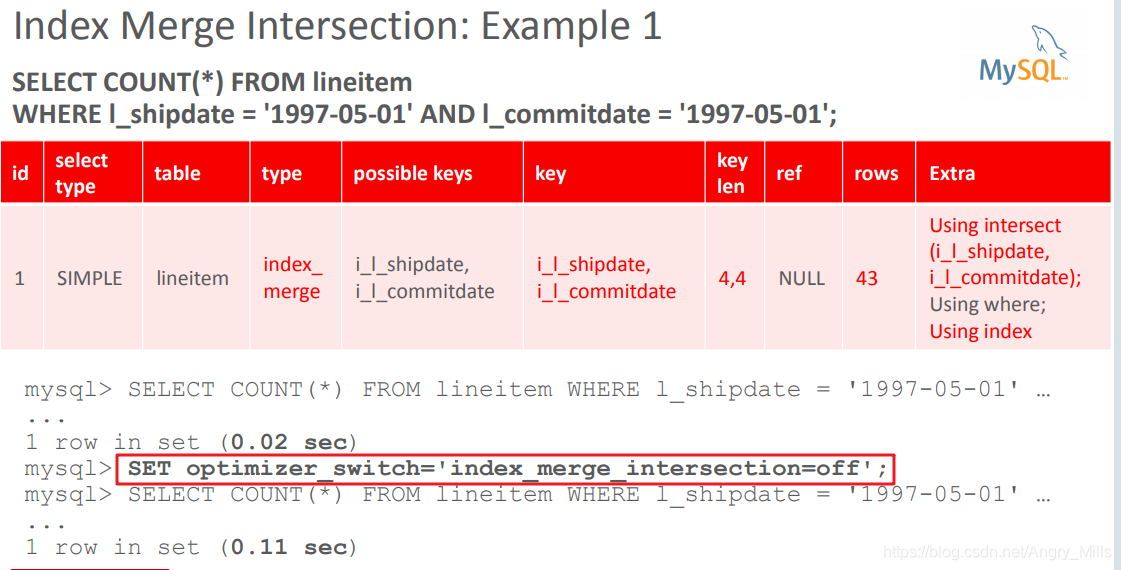
Example1:
图 Index Merge Intersection Example 1
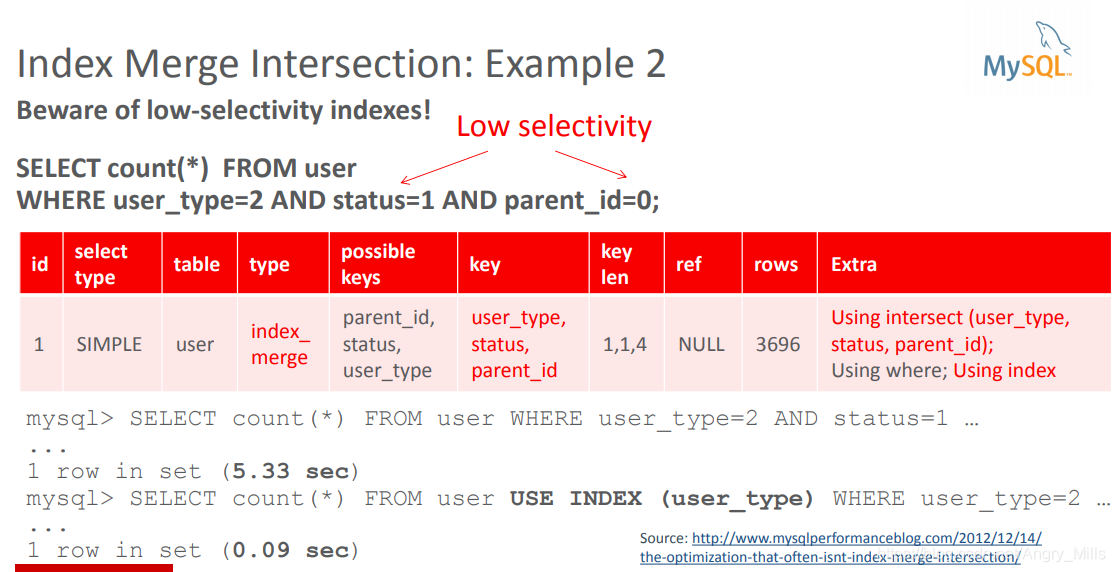
Example2:
Beware of low-selectivity indexes!
图 Index Merge Intersection Example 2
Example3:
Handler status variables
图 Index Merge Intersection Example 2+

”Greedy search strategy”
目的: Given a JOIN of N tables, find the best JOIN ordering
- Strategy: 策略:
- Start with all 1-table plans (Sorted based on size and key dependency)
- Expand each plan with remaining tables
- If “cost of partial plan” > “cost of best plan”:
- Heuristic pruning:
- Prune less promising partial plans
- May in rare cases miss most optimal plan (turn off with set optimizer_prune_level = 0)
JOIN Optimizer Illustrated 连接优化器插图
图 Join Optimizer
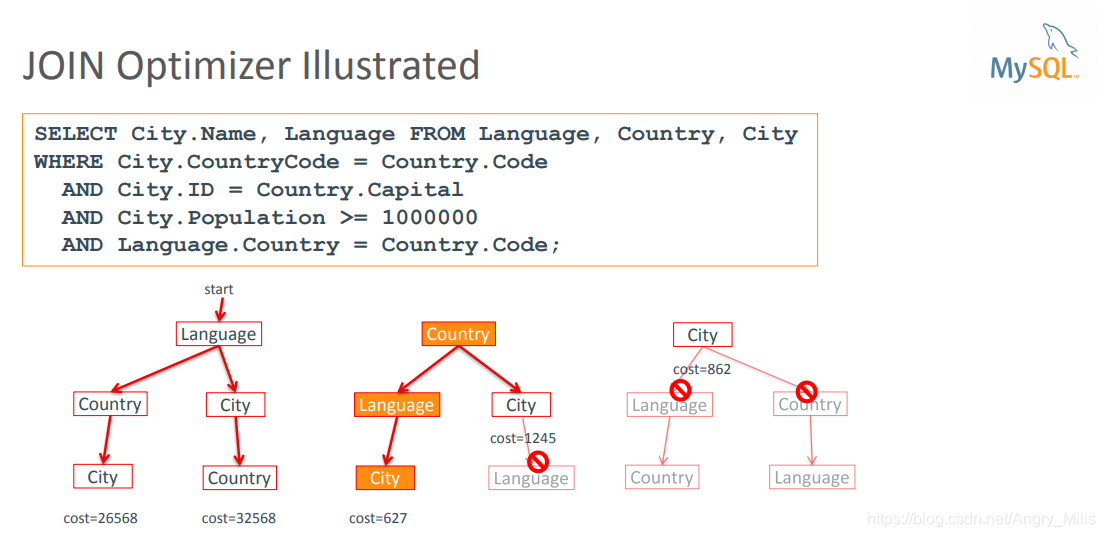
Change join order with STRAIGHT_JOIN
图 Join Optimizer+
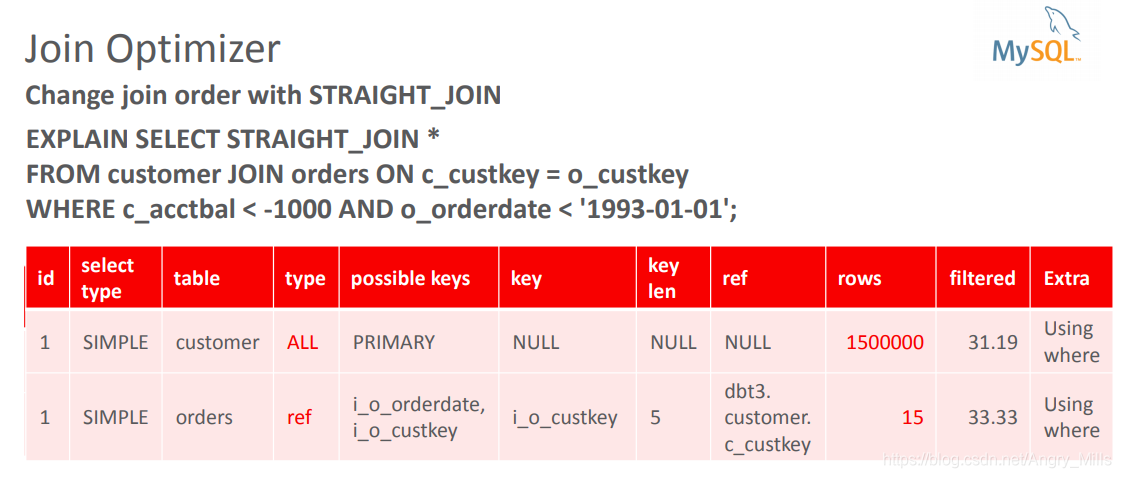
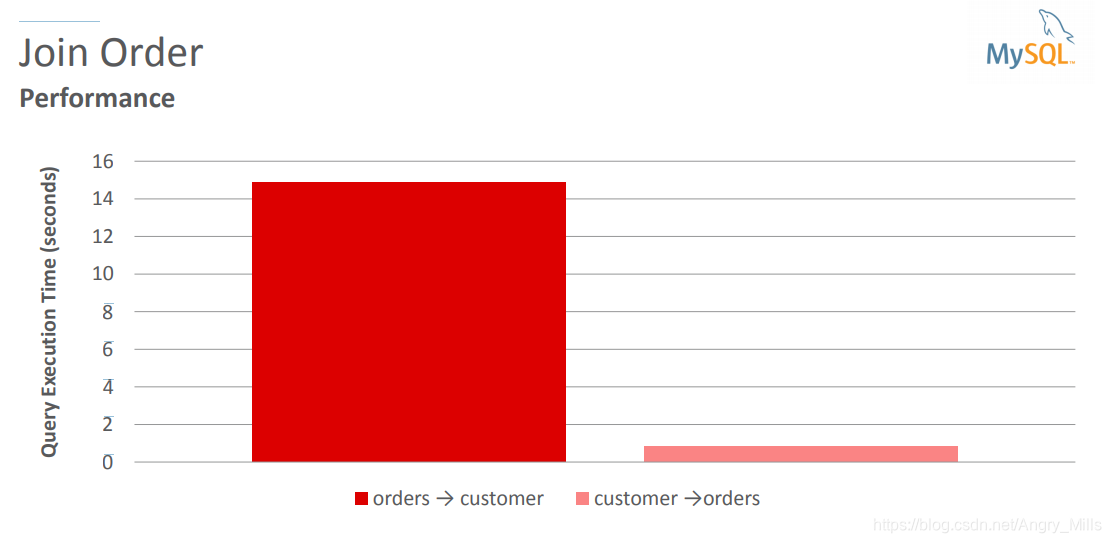
Join Order
图 Join Order
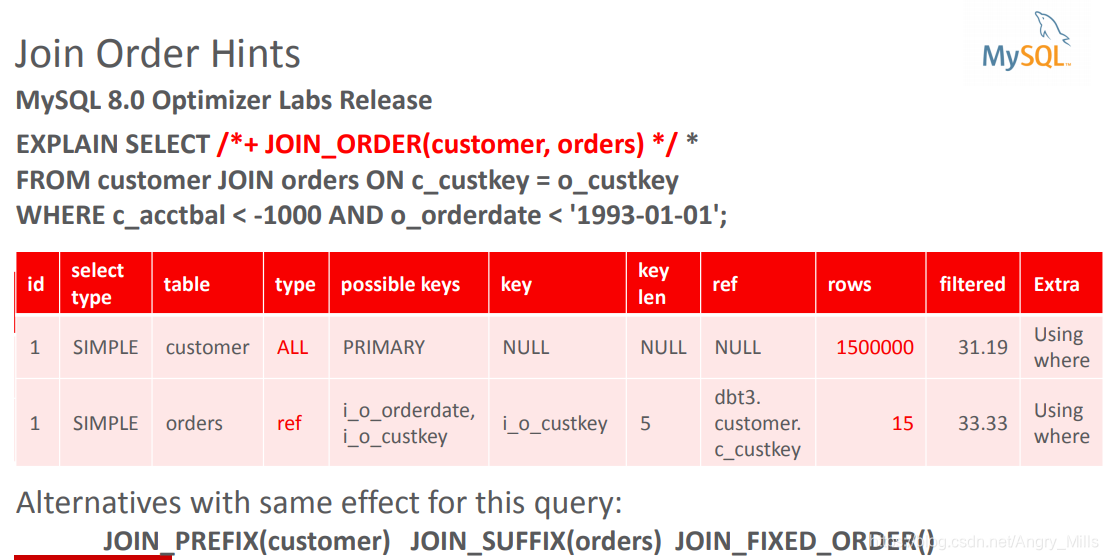
Join Order Hints
MySQL 8.0 Optimizer Labs Release
- Alternatives with same effect for this query:
图 Join Order Hints
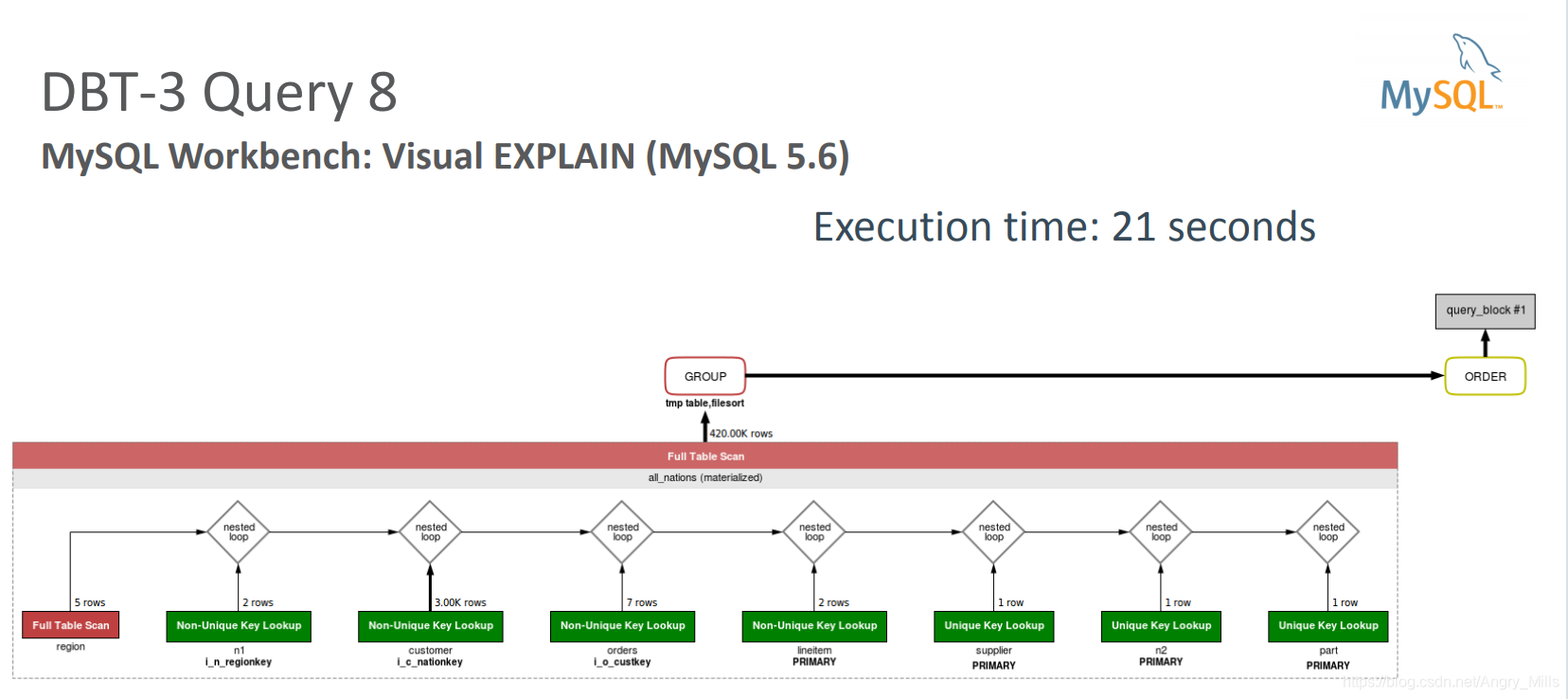
National Market Share Query
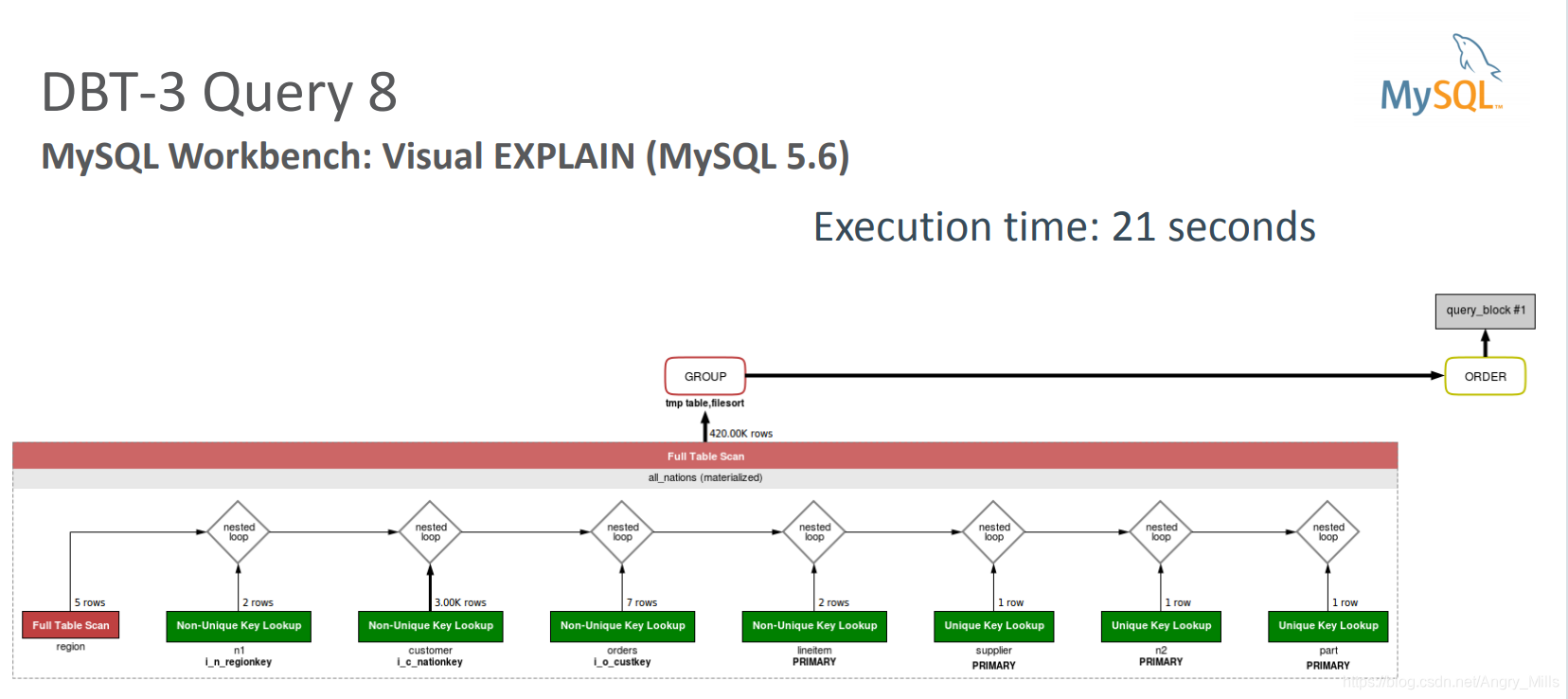
MySQL Workbench Visual EXPLAIN MySQL Workbench
图 MySQL Workbench: Visual EXPLAIN
Force early processing of high selectivity conditions
图 Force early processing of high selectivity conditions

Improved join order
图 Improved join order
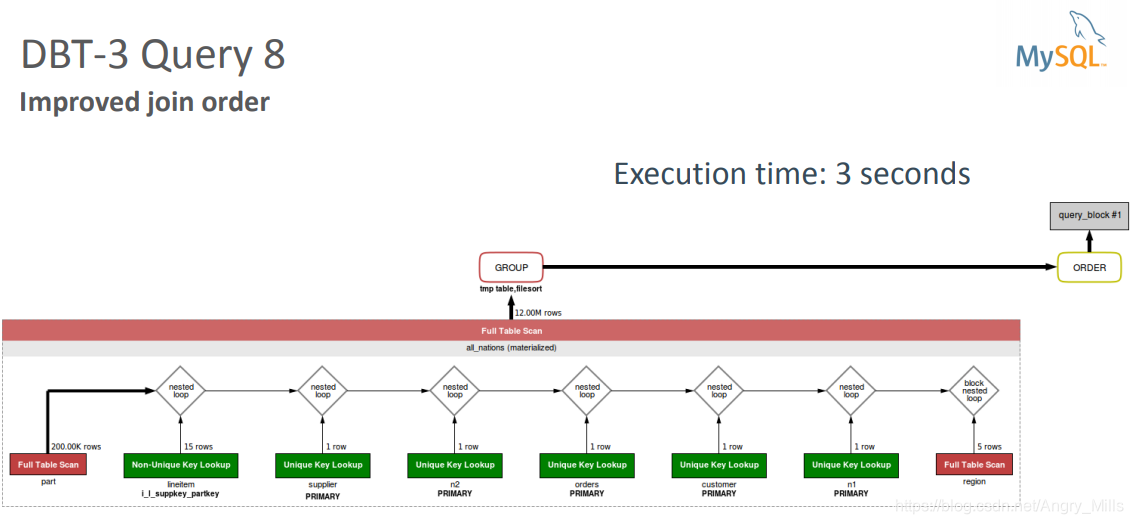
- Improvements to Query 8 in MySQL 5.7:
- Filtering on non-indexed columns are taken into account
- No need for hint to force part table to be processed early
- Merge derived tables into outer query
- No temporary table
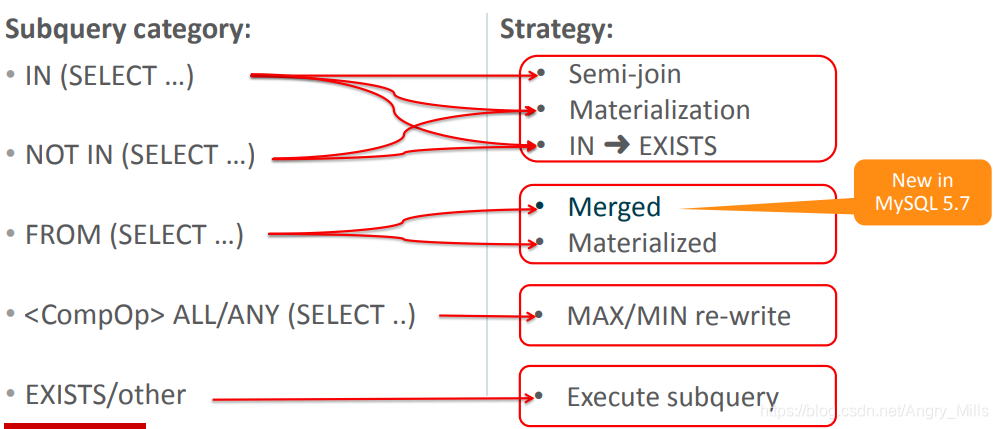
Overview of Subquery Optimizations
| Subquery category: | Strategy: |
|---|
| IN (SELECT …) | Semi-join Materialization |
| NOT IN (SELECT …) | IN ? EXISTS |
| FROM (SELECT …) | Merged Materialized |
| ALL/ANY (SELECT …) | MAX/MIN re-write |
| EXISTS/other | Execute subquery |
图 Subquery category
- Traditional Optimization of IN Subqueries
- IN -> EXISTS transformation
- Convert IN subquery to EXISTS subquery by “push-down” IN-equality to
subquery 优化为 => - Benefit: subquery will evaluate fewer records
- Note: Special handling if pushed down expressions can be NULL
Semi-join
-
Convert subquery to inner join, BUT Need some way to remove duplicates
-
Different strategies for duplicate removal:
- FirstMatch (equivalent to IN→EXISTS execution)
- LooseScan (index scan, skip duplicates)
- Materialization: MatLookup (like subquery materialization), MatScan
(materialized table is first in join order)
- Duplicate WeedOut (insert result rows of semi-join query into
temporary table with unique index; duplicate rows will be rejected.
Any join order.)
-
If duplicate removal is not necessary:
Main advantage :
- Opens up for more optimal ”join orders”
例如:
- Will process less rows if starting with lineitem instead of orders
- Restriction: 限制:
- Cannot use semi-join if subquery contains union or aggregation
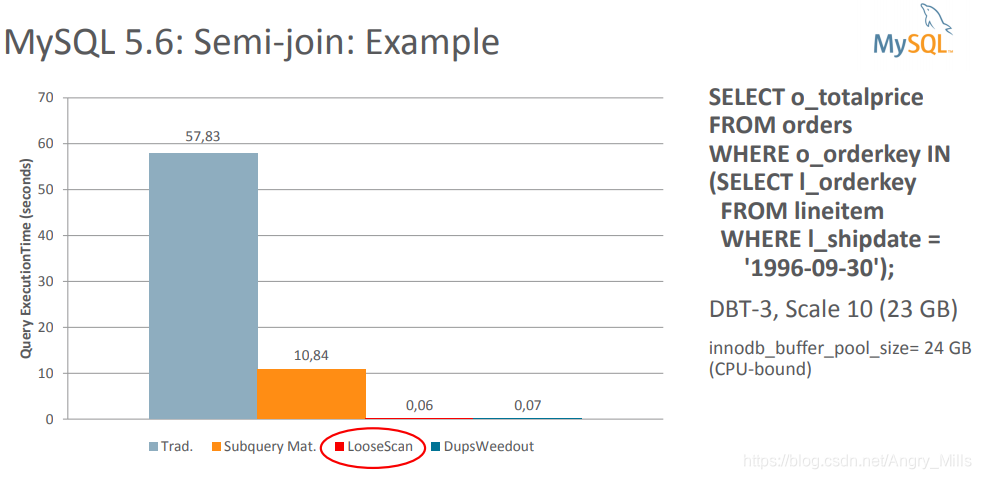
MySQL 5.6: Semi-join: Example
图 MySQL 5.6: Semi-join: Example
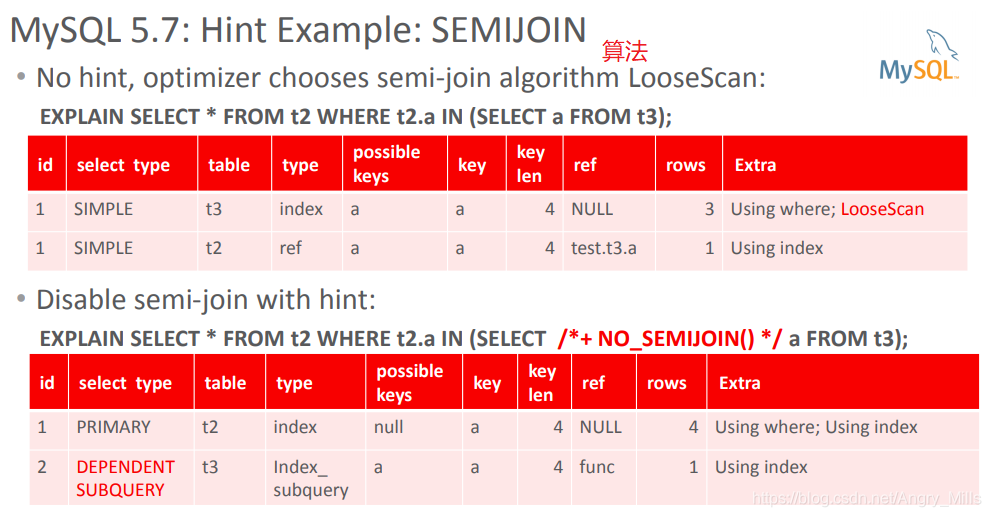
MySQL 5.7: Hint Example:
- No hint, optimizer chooses semi-join algorithm LooseScan:
- Disable semi-join with hint:
图 Hint Example: SEMIJOIN
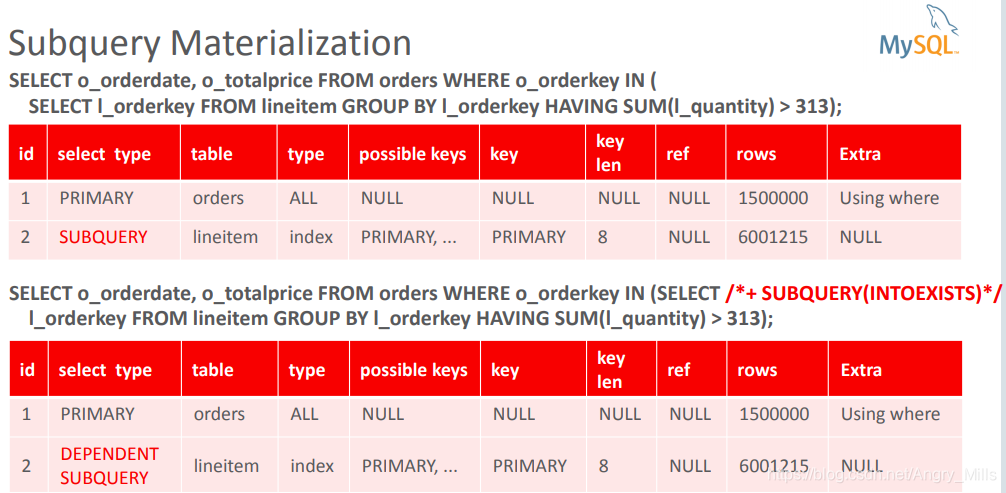
- Subquery Materialization
- Execute subquery once and store result in a temporary table
- Table has unique index for quick look-up and duplicate removal
- Execute outer query and check for matches in temporary table
图 Subquery Materialization
比较子查询实现和IN?EXISTS 比较IN —> EXISTS的实现

图 Comparing Subquery Materialization
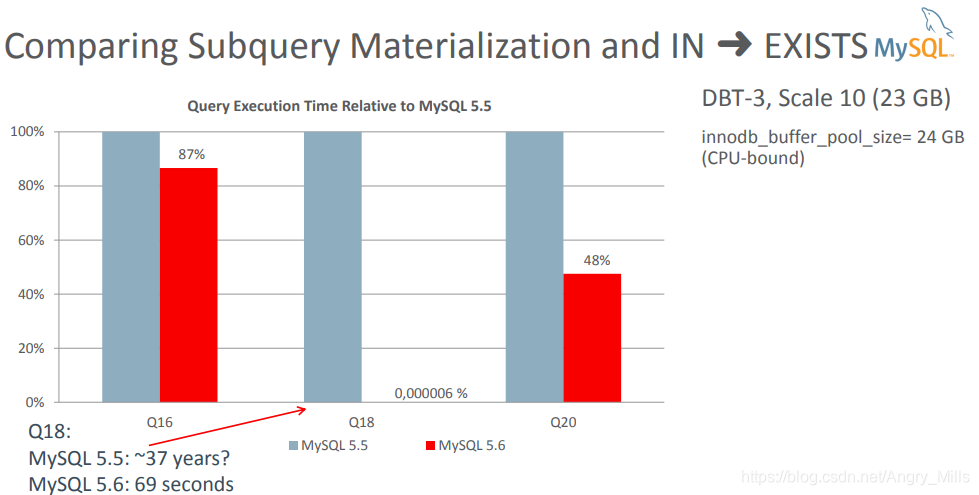
图 Subquery Materialization+
Derived Tables
- Subquery in FROM clause
- MySQL 5.6 and earlier: Executed separately and result stored in a
temporary table (materialization) - MySQL 5.7: Treat derived tables like views: May be merged with outer
query block
图 Index on Materialized Derived Table
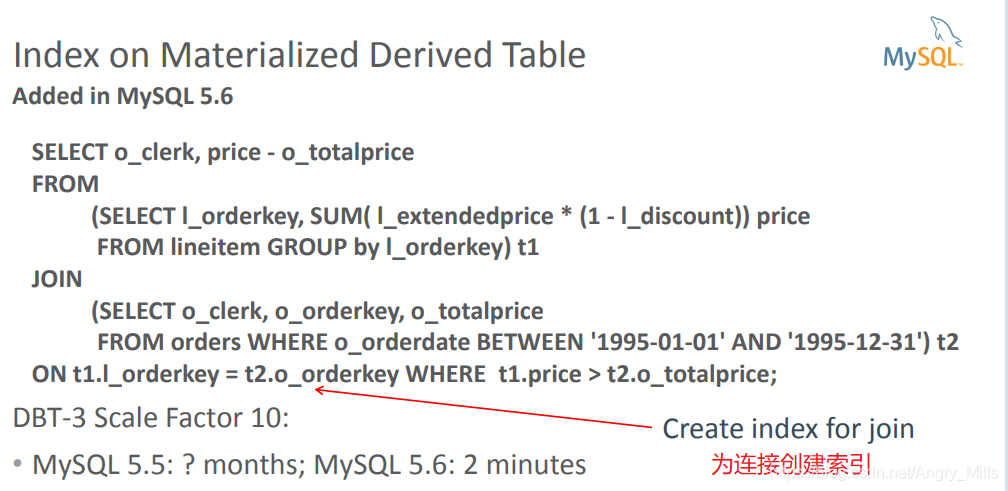
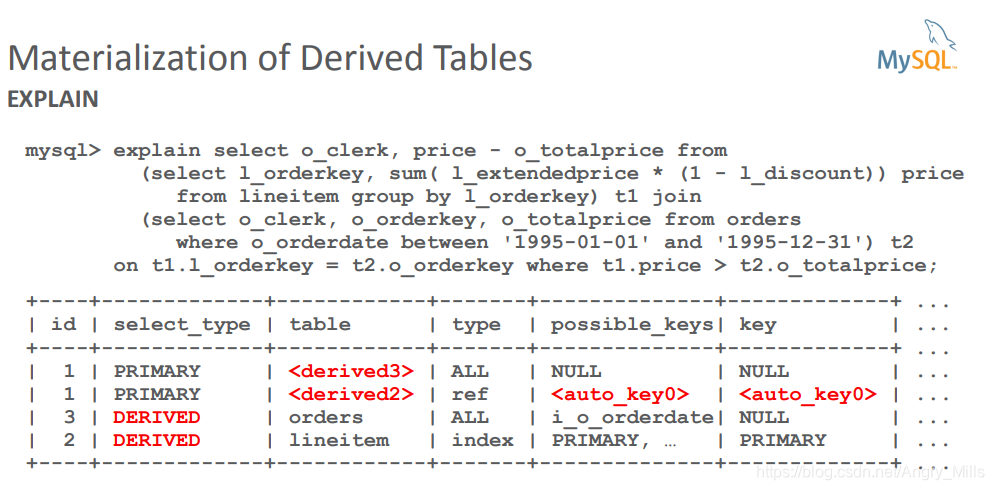
图 Materialization of Derived Tables EXPLAIN
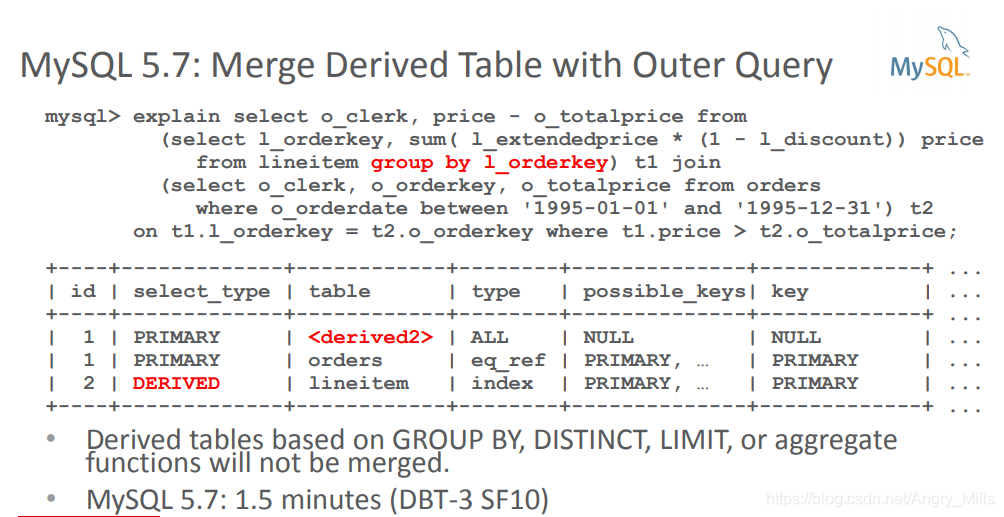
- Merge Derived Table with Outer Query
- Derived tables based on GROUP BY, DISTINCT, LIMIT, or aggregate
functions will not be merged
图 Merge Derived Table with Outer Query
Hint: Merge/Materialize Derived Table or View
- MySQL 8.0.0 optimizer labs release
-
Derived tables/views are, if possible, merged into outer query
-
NO_MERGE hint can be used to override default behavior: :
-
MERGE hint will force a merge
-
Can also use MERGE/NO_MERGE hints for views
ORDER BY Optimizations
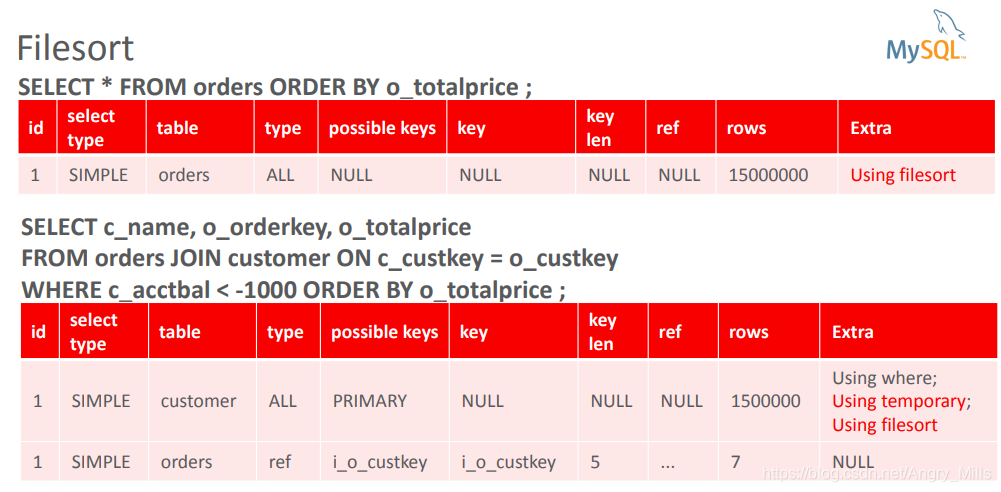
- General solution; “Filesort”:
- Store query result in temporary table before sorting
- If data volume is large, may need to sort in several passes with intermediate storage on disk.
- Optimizations :
- Take advantage of index to generate query result in sorted order
- For ”LIMIT n” queries, maintain priority queue of n top items in
memory instead of filesort. (MySQL 5.6)
Filesort
图 Filesort
Status variables
图 Filesort+

Performance Schema
图 Filesort Performance Schema
Sorting status per statement available from Performance Schema

案例1
图 Filesort Case Study1

案例2
图 Filesort Case Study2

案例3
图 Filesort Case Study3
Increase sort buffer
默认256 KB。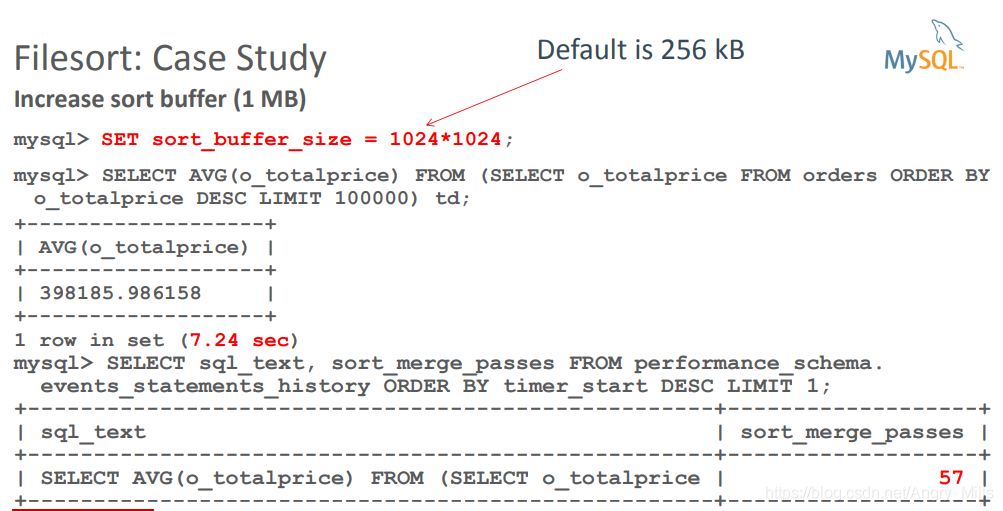
案例4
图 Filesort Case Study4
Increase sort buffer even more (8MB)

图 Using Index to Avoid Sorting
Using Index to Avoid Sorting
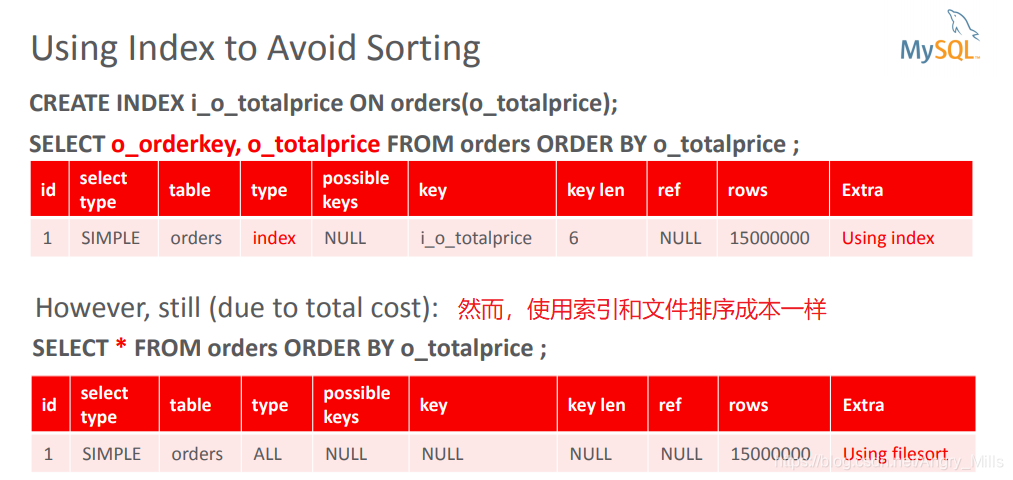
图 Using Index to Avoid Sorting Case study
Case study revisited

- Add indexes
- Force use of specific indexes:
- USE INDEX, FORCE INDEX, IGNORE INDEX
- Force specific join order:
- Adjust session variables
- optimizer_switch flags: set optimizer_switch=“index_merge=off”
- Buffer sizes: set sort_buffer=810241024;
- Other variables: set optimizer_search_depth = 10;
MySQL 5.7: New Optimizer Hints
Optimizer Hints
- Future :
- New hints in 8.0.0 Optimizer Labs Release
- Enable/disable merge of views and derived tables:
- MERGE() NO_MERGE()
- Join order
- Hints we consider to add
- Force/ignore index_merge Alternatives
- Reimplement index hints in new syntax
- Temporarily set session variables for just one query
MySQL 5.7: Query Rewrite Plugin
图 Query Rewrite Plugin

- New pre- and post-parse query rewrite APIs
MySQL 5.7: Adjustable Cost Constants
Experimental! Use with caution! No guarantees
图 Adjustable Cost Constants
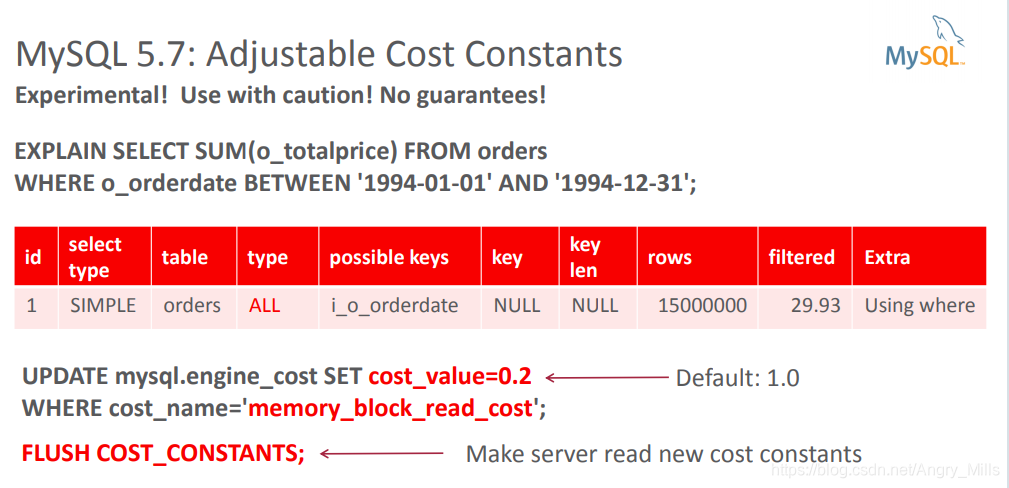
图 Adjustable Cost Constants+

More information 更多信息:
-
MySQL Server Team blog
-
http://mysqlserverteam.com/
-
My blog:
-
http://oysteing.blogspot.com/
-
Optimizer team blog:
-
http://mysqloptimizerteam.blogspot.com/
-
MySQL forums:
-
Optimizer & Parser:
http://forums.mysql.com/list.php?115/
-
Performance:
http://forums.mysql.com/list.php?24/



